Your heart plays an important role in your overall health. It is responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to each cell of your body. The heart achieves this through an intricate web of arteries and veins known as the cardiovascular system. With the key role that the heart plays in maintaining overall health, it is essential for you to take care of your heart. However, the modern sedentary lifestyle coupled with poor dietary habits and the constant presence of stress poses a significant risk to the health of your heart. This overworked, stressful modern lifestyle has brought heart conditions from far future old age to our doorsteps in the age of 30s.
Wondering what factors affect your heart health and how can omega-3 helps mitigate the effects? Dive right in for a healthier heart.
Factors Affecting Heart Health
Multiple factors such as proper diet, lifestyle, family history, play key roles in maintaining your heart health. Watch out for below factors that can affect your heart health [1] [2] –
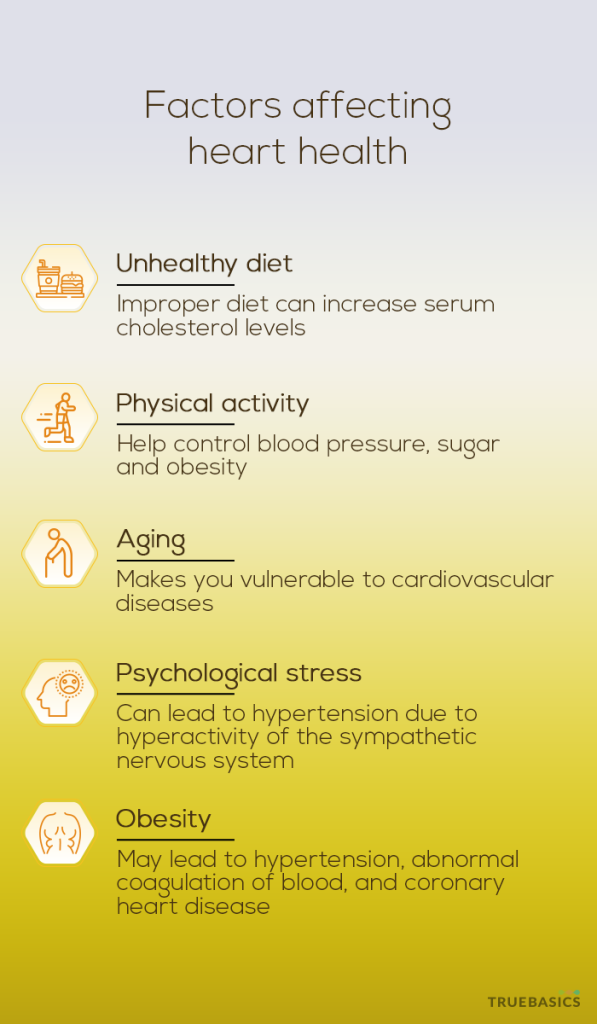
1. Unhealthy Diet
Your daily dietary intake can significantly influence your heart health. Whether it is a positive influence or negative influence, is completely dependent on your food intake and dietary habits.
If your diet is replete with foods that have high amounts of saturated fats as well as high sodium content, then you may be causing damage to your heart. A diet rich in saturated and trans fats often leads to an increase in serum cholesterol levels which makes you vulnerable to coronary heart disease. A high sodium diet can cause hypertension (high blood pressure) which is often a precursor to cardiovascular diseases.
Avoiding high fat and high salt food and intake of a healthy diet, rich with omega-3, antioxidants, and key vitamins & minerals can help reduce the risk of heart conditions and maintain a healthy heart. [3]
2. Physical Activity
Regular, moderate physical аctivity is great for your heart health. When you’re active and your body is in motion, there’s better blood flow in the blood vessels of your heart. The heart pushes more blood to the body in every beat, which slows down the heartbeat and controls blood pressure. Also, when you indulge in a workout regularly, your body tissues work better in extracting oxygen from the blood and keeps your heart in the good working condition under stress. [4]
3. Aging
Aging has a profound effect on your cardiovascular health. Aging makes you vulnerable to cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries), hypertension, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and a stroke. With age, heart’s cardiac output decreases, walls of arteries thicken, arteries become inelastic, heart size increases, cell death due to oxidative stress increases, and impaired blood filling capacity in the left ventricle. [5] [6]
4. Psychological Stress
Stress has a significant impact on your cardiovascular health. Chronic stress leads to hyperactivity of your sympathetic nervous system which in turn leads to high blood pressure as well as exaggerated heart rates. This has been linked to the accelerated development of atherosclerosis in humans. According to a study, psychosocial stresses tend to cluster together resulting in an elevated cardiovascular risk. [7]
5. Obesity
Obesity is one of the leading precursors of cardiovascular diseases. Obesity has been linked with multiple precursors of heart related issues such as dyslipidemia (abnormal amounts of lipids), hypertension, glucose intolerance, inflammatory markers, obstructive sleep apnea, and the prothrombotic state (abnormal coagulation of blood) [8]. Studies have reported that obesity also increases the risk of cardiac complications such as coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure. [9]
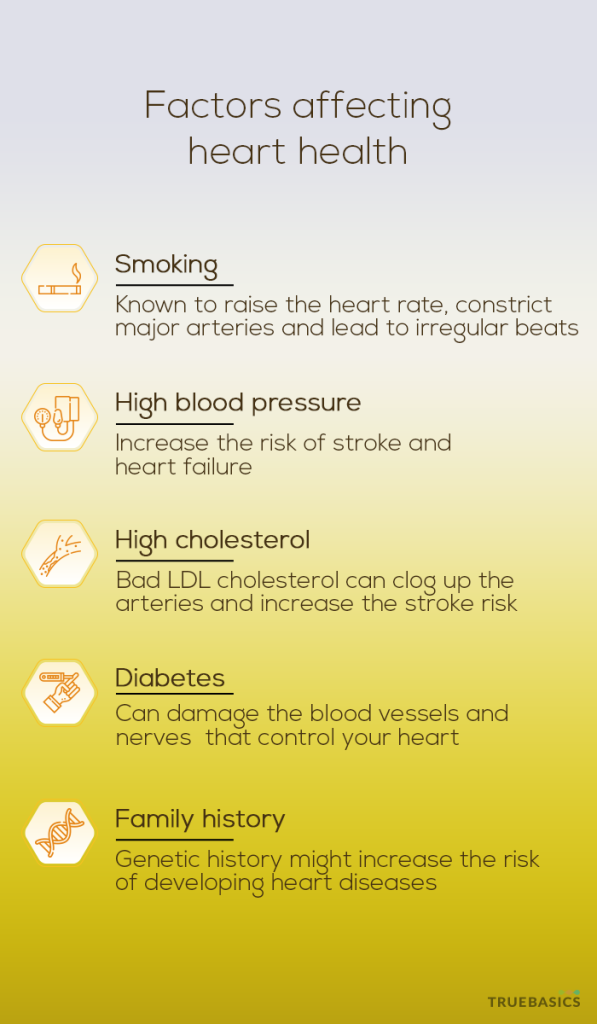
6. Smoking
Smoking is known to raise the heart rate, constrict major arteries, and lead to irregular beats or rhythms. This not only makes your heart work harder for the same amount of work than a non-smoker but also raises your blood pressure which can increase the risk of strokes. Smoking can also be a major contributor to coronary heart disease.
7. High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is often a precursor to heart conditions and can have detrimental effects on your cardiovascular health. Blood pressure is produced primarily by the contraction of the heart muscles. An elevation in blood pressure, аlso known as hypertension, can lead to heart conditions like stroke, heart attack, and heart failure. It can also lead to other conditions such as narrowed blood vessels in the kidney and dementia. [10]
When there’s no proper blood flow to your heart, you experience chest pain and irregular heart rhythms, which can lead to a heart attack. When the pressure in your blood veins is higher, it causes your heart to pump blood faster, which further thickens the left ventricle of the heart. This puts your heart at a greater risk of a heart attack. [11]
8. High Cholesterol
Cholesterol (LDL and HDL cholesterol) is present in every cell of the body and has important naturаl functions when it comes to digesting foods, producing hormones, and generating vitamin D. At normal levels, it is an essential substance for the body. However, if cholesterol concentrations in the blood get too high, it becomes a silent danger that puts you at an increased risk of heart conditions.
An excessive amount of LDL or “bad” cholesterol can clog up the arteries that feed your heart and brain, increasing the risk of stroke and heart аttack.[12]
9. Diabetes
The presence of high blood sugar levels can affect heart health. Diabetes develops when there is too much sugar in the blood because the body either fаils to make enough insulin or cannot use it efficiently. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate depending on the time of day, what you eat аnd when you eat it. Too high or too low a level can affect your concentration, make you dizzy, and harm vital organs. The diabetic high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels that control your heart and put you at a greater risk of heart diseases.[13]
10. Family History
If someone in your family, your blood relatives, has had a history of heart conditions, then there is an increased risk of you inheriting the cardiovascular conditions as well.
Family history is considered a risk-enhancing factor in cardiovascular diseases. Genetic affects your propensity to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and influence lipid levels as well. However, certain studies have reported that genetic risk factors can be offset by a healthy lifestyle, good diet, and physical activity. [14]
Role of Omega-3 In Heаrt Health
Omega-3 fаtty acids are found in both marine and plant-based foods and oils. Omega-3 are polyunsaturated fatty acids and have anti-inflammatory properties [15]. Omega-3 is known to have multiple benefits for heart health.
1. Manages cholesterol levels
Intake of omega-3 fatty acids help lower triglycerides and manage cholesterol levels. They increase the levels of “good” HDL cholesterol and can also reduce “bad” LDL cholesterol levels [16].
2. Lowers triglyceride levels
The most consistent evidence for omega-3 and heart health is their аbility to lower triglyceride levels. High levels of triglycerides have been linked with a fatty build-up in the artery walls, which increases your risk of heart аttack and stroke [17]. Omega-3, owing to its antiatherogenic (prevention of fatty degeneration of arteries) properties, can help reduce the triglycerides levels. [18]
3. Lowers blood pressure
High blood pressure can lead to heart attack and stroke. Omega-3 can help with the lowering of blood pressure levels. Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce arterial stiffness and the abnormal accumulation of plaque in the arteries to modulate healthy blood pressure [19]. Studies have reported that both systolic blood pressure (pressure in arteries when heart muscles contract) and diastolic blood pressure (the arterial pressure between the beats) show dramatic reduction when omega-3 is included in the diet. [20]
4. Regulates heartbeats
Omega-3 fatty acids have been known to reduce electrical excitability inside the cell membranes of the cardiac myocyte and lower the resting membrane potential. It also lowers the refractory period (resting period of heart cells) by inhibiting the ion channels, thus regulating the heartbeats. [21]

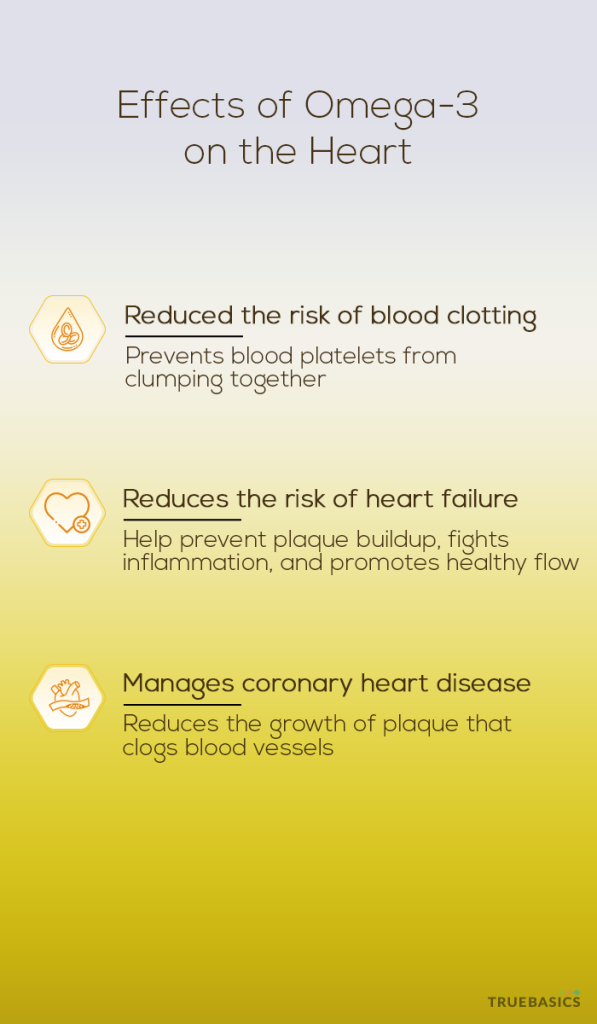
5. Reduces the risk of blood clotting
Omega-3 fatty acids help prevent blood platelets from forming a clump together. Clotting in the arteries can lead to thick, hard arteries and consequently lead to coronary heart disease or CHD [22]. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-thrombotic properties (prevents blood clotting) and antiatherogenic effects. Because of these properties, omega-3 keeps the lining of the arteries smooth and free of damage.
6. Reduces the Risk of heart failure
Heart failure is a common and growing public health problem worldwide. Despite advances in pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies, the treatment of heart failure remains a challenge thereby necessitating a need for preventive measures for heart health. Health authorities, including the Indian Council of Medical Research, have long recommended consumption of omega-3 rich diet to provide cardiovasculаr protective effects [23]. Omega-3 fatty acids have antidysrhythmic, antiatherogenic, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and endothelial protective effects. Omega-3 helps prevents irregularities in heart rhythms, abnormal plaque buildup in arteries, fight inflammation and promote healthy blood flow thereby reducing the risk of heart failure. [24] [25] [26]
7. Manages Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is the condition that develops when the arteries become too narrow and hardened and constrict the normal blood flow. CHD is generally caused by cholesterol deposits (plaque buildup) in the artery walls that are responsible for supplying blood to the heart [27]. Omega-3 helps reduce the growth of plaque that obstructs blood flow.
ICMR recommends an increased intake of Omega-3 for heart health 24. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends has recommended everyone to consume Omega-3 rich foods (fishes, mostly) at least twice a week. If you have any heart condition or generally suffer from high triglyceride levels, you need to include Omega-3 fatty acids in your diet most of all. Consult your doctor for the recommended dosage of omega-3.
Sources of Omega-3
Following are the top dietary sources of omega-3
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Cod Liver Oil
- Shrimp
- Tuna
- Flaxseed oil
- Canola oil
- Walnuts
In Conclusion…
Omega-3 fatty acids play key roles to help lower the risk of heart disease. They are essential for healthy heart function due to their cardioprotective properties. Not only do they help reduce the risk of coronary heart disease, but they also protect the heart against aging and the damage caused by chronic stress. Regular intake of Omega -3 fatty acids along with a healthy lifestyle and behavioral changes can help you manage and prevent cardiovascular damage and may lead to healthy heart function.
It’s time to choose your heart!
Sources:
[1] https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/risk_factors.htm
[2] https://www.world-heart-federation.org/resources/risk-factors/
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4248376/
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3396114/
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3223374/
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3366686/
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10217662
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12361492
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16380542
[10] https://omegaquant.com/new-research-finds-link-omega-3-index-blood-pressure/
[11] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/high-blood-pressure/art-20045868
[12] https://www.verywellhealth.com/can-fish-oil-omega-3-fatty-acids-lower-cholesterol-698137
[13] https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/heart-disease-stroke
[14] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5338864/
[15] https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-omega-3-fatty-acids
[16] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5745982/
[17] https://www.tctmd.com/news/new-aha-guidance-omega-3-fatty-acids-high-triglycerides
[18] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3875260/
[19] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6085127/
[20] https://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/news/20070604/omega-3-may-lower-blood-pressure
[21] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3483717/
[22] https://omegaquant.com/do-omega-3s-thin-the-blood/
[23] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5345296/
[24] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20500789
[25] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4418670/
[26] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3875260/
[27] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613