Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids and carry multiple benefits for heart, joints, brain, skin, and eye health. Omega-3 fatty acids are called essential because your body can’t make them, and they can only be obtained through external sources. Fish oil has shot to fame because of the inadequacy of enough omega-3 from food sources. Fish oil is the oil extracted from fatty fishes. It is often used as a dietary supplement for fulfilling the omega-3 requirement. Few good sources of fish oil include – Sardines, Tuna, Lemuru, Capelin, Polar Cod, Saithe, Mackerel, Herring, and Sprat
What is Fish Oil?
Indian Council of Medical Research, owing to multiple health benefits of omega-3, has stressed on increasing the intake of omega-3. It can be difficult to maintain appropriate levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the body through diet alone, especially considering the Indian dietary patterns [1]. The majority of the Indian population is either vegetarian or does not consume fish regularly. This leaves only plants as omega-3 sources (in the form of ALA). ALA is synthesized into EPA and DHA. However, the conversion is inefficient and not enough to fulfill the body’s requirement of the essential fatty acids. According to studies, only about 20% of ALA is converted to EPA and only up to 9% of ALA is converted to DHA [2]. Fish oil, therefore, offers an alternative source to meet the gap in EPA/ DHA intake and fulfill the Omega-3 requirement. The main benefit of fish oil is its high content of EPA and DHA which usually ranges from 18 – 31%. [3] [4]
However, with the knowledge of the benefits of fish oil, various misinformation, myths, half-truths have also sprung up. Wondering what are the key fish oil myths and if you have had any of them? Dive right in to bust 9 common myths around omega-3 and fish oil.
Myth #1: All omega-3 sources are equally important
Reality: Different omega-3 sources contain different forms of Omega-3, i.e. ALA, EPA & DHA and offer different benefits
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the most easily accessible Omega-3, available through plant sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, soybean, and canola oil [5]. ALA is primarily used by the body as a source of energy. ALA is also converted to more functionally active forms of omega-3 – Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) & docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the human body [6]. However, the conversion process is highly inefficient with only up to 20% conversion to EPA and up to 9% for DHA. It can be derived from one’s daily dietary intake.
EPA is mostly obtained from marine sources. EPA plays a key role in cellular inflammation. It inhibits the supply of arachidonic acid required for the synthesis of inflammatory eicosanoids. EPA also has beneficial effects in the case of mood-related disorders. EPA and DHA can be found in cold-water fish like mackerel, sardines, herring, salmon, tuna, anchovies.
DHA is one of the most important Omega-3 fatty acids. The brain and eyes have significantly higher DHA levels as compared to other organs. DHA is especially concentrated in the grey matter of the brain and in the retina. It is the structural component of the human nervous system. It is essential for the growth and development of the brain in infants as well as the maintenance of normal brain function in adults. DHA is also responsible for the quality of one’s vision [7]. DHA is also known for its antidysrhythmic, antiatherogenic, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and endothelial protective effects that promote healthy heart function by preventing irregularities in heart rhythms, abnormal plaque build-up in arteries, fighting inflammation and promoting healthy blood flow. Fatty fishes such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel are the primary sources of DHA.
Myth #2: Taking fish oil will increase body weight
Reality: Taking fish oil doesn’t increase weight. On the contrary, it can help control metabolism and lose weight
Omega-3 is known to increase serotonin levels in the body. Serotonin curbs cravings and make your stomach feel full. If you often feel hungry then including omega-3 in diet can help to avoid overeating and eating at off-hours. Omega-3 present in the fish oil can help improve your metabolic system and therefore can help burn more calories and lose excess weight [8]. Also, obesity and associated cardiovascular issues create inflammatory pathways in the body. Omega-3, due to its anti-inflammatory properties, can help also manage issues arising due to obesity. [9]
Myth #3: Eating fish is the best way to get omega-3 fatty acids
Reality: Not all fishes have optimum amounts of omega-3 to fulfill your required dietary intake.
Usually, there is a wide gap between the amount of Omega-3 necessary for the healthy functioning of the human body and what you may get from your daily dietary intake. Eating fatty fish is a good way to increase your omega-3 intake. However, not all fishes have enough omega-3 content to meet the daily dietary requirement. Cold-water, fatty fishes are a rich source of omega-3. You should check the nutritional value of the consumed fish if you are a regular fish eater. Fish are also susceptible to seawater contamination. Heavy metal like mercury can enter the fish system which then transfers to the human body when fishes are consumed.
Fish also don’t form a part of the daily diet for the majority of the Indian population. It is not a viable option for a large portion of the Indian population following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle. The fish is also not part of a daily diet even among non-vegetarian. Also, think of the taste buds if you’re planning to have fish 1-2 times every day!

Myth #4: Little omega-3 is better than nothing
Reality: Benefits of Omega-3 are dependent on the amount of Omega-3 intake. [10]
Reaping the benefits of omega-3 intake requires a certain dosage amount and therefore depends on the amount of omega-3 intake. To illustrate, omega-3 compete for the same enzyme sites as pro-inflammatory compounds such as omega-6 fatty acids on a molecular level to carry out anti-inflammatory functions. Omega-6 is pro-inflammatory in nature and therefore an excess of omega-6 can trigger inflammatory action in the body thus countering the positive effects of omega-3. [11]
If the dose is less than the required amount, omega-3 fatty acids might not be able to perform their intended functions for the associated benefits. Certain studies have also reported that anxiety patients experienced significant clinical benefits when they consumed omega-3 doses greater than 2000 mg EPA/DHA daily. Studies have also reported similar associations with omega-3 dosage for reaping the benefits at a cellular level of anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3. [12]
Myth #5: Concentrated fish oils are always superior
Reality: Concentrating the omega-3 may strip off the natural spectrum of Omega-3 and pose problems due to their synthetic nature.
Concentrated forms of fish oil have gained public favor as they deliver higher amounts of EPA and DHA as compared to natural fish oils. Concentrating the fish oil helps to consume higher EPA/DHA per serving of capsules. However, excessive concentrating of fish oil can reduce overall bioavailability and remove other natural omega-3 fatty acids. The synthetic nature of concentrated fish oil can also pose a certain risk to pregnant women and infants. Before opting for concentrated forms of fish oil, consult with your doctors for the appropriate dosage amount or opt for natural fish oils.
Myth #6: Fish oil supplements only help with heart issues
Reality: Fish oil supplements also help in maintaining brain, joint, eye and skin health
While cardioprotective benefits of omega-3 are well known, the benefits of fish oil are not limited only to heart health. Consumption of omega-3 and fish oil can also help with brain, joint health, eye, and skin health.
DHA is a key component of brain structure. DHA from Omega-3 is important for the development of the brain during infancy and proper brain functioning throughout adulthood. It can also help in the prevention of brain aging and cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia. [13]
Omega-3 helps reduce inflammation in joints thus relieving joint stiffness and pain. Omega-3 can also help in joint-related issues like rheumatoid arthritis. They inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines responsible for the pain caused by arthritis. [14]
DHA is integral for eye development, especially retina. DHA is a major constituent of the tissues of the eyes. Omega-3 also helps reduce dry eye symptoms including burning and redness. They promote vessel regrowth after injury, synthesize disk membranes, promote conformational rhodopsin changes, and modify the activity of retinal enzymes [15]. DHA can also help prevent Age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The retina of the eyes uses DHA for continuous renewal of photoreceptors (the cells in the retina which respond to light)
Omega-3 plays an essential role in protecting the skin against UV induced damage, skin hydration, and strengthening the skin cells. It can also help in reducing acne and prevention of skin-related issues such as photoaging and dermatitis. [16]

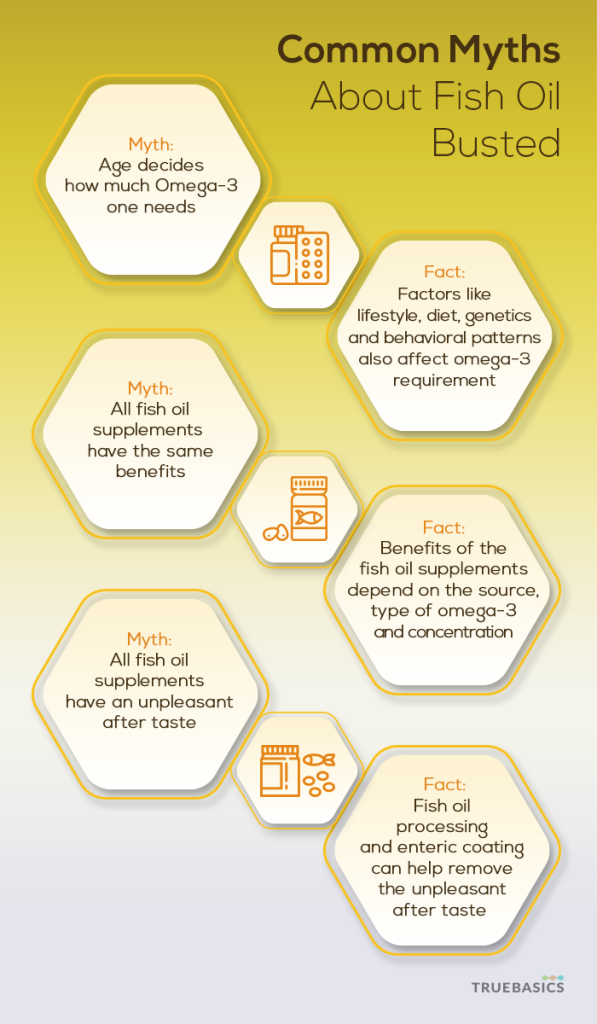
Myth #7: Age decides how much omega-3 one needs
Reality: While age is a factor in deciding on the dose for Omega-3, it is not the only deciding factor. Factors like lifestyle, diet, genetics and behavioral patterns also affect omega-3 requirements.
The amount of omega-3 requirement depends on multiple factors. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, physical activity, and stress-free life can reduce the omega-3 requirement while heavy consumption of fast food (which is rich in omega-6 and are damaging for heart health), smoking, chronic stress and excessive consumption can increase the requirement. The sought benefit from omega-3 is also an important factor in determining the omega-3 requirement. Omega-3 helps in heart, joint, brain, eye, skin health and inflammation through a different mechanism and therefore your omega-3 dosage may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Myth #8: All fish oil supplements have the same benefits
Reality: Benefits of the fish oil supplements depend on the source, type of omega-3 and concentration.
It is important to understand your fish oil constituents to reap the maximum benefits of omega-3. Different fish oil supplements may have varying benefits depending on their source, form, EPA/DHA/ALA content. Fish oil supplements typically vary in source, type of omega-3 (ALA vs EPA/DHA), omega-3 content, form (such as triglycerides, free fatty acids, ethyl esters, etc.), purity, freshness, and coating. For instance, Krill oil is extracted from the Antarctic Krill [17]. It provides EPA and DHA in triglyceride and phospholipid forms which are easily absorbed by the human body. EPA and DHA are more functionally active than ALA therefore ensure that your omega-3 supplement has EPA/DHA in it.
Myth #9: All fish oil supplements have an unpleasant aftertaste
Reality: Fish oil supplements need not necessarily have an unpleasant aftertaste.
The unpleasant aftertaste of fish oil supplements can be due to either rancid fish oil or premature digestion in the stomach. If your fish oil supplement is beginning to taste rancid, it has probably started to oxidize or go bad. Check for the freshness of the fish oil before further consumption.
Fish oil processing and enteric coating can also help remove the unpleasant aftertaste. Enteric coating prevents the fish oil capsule from digesting before it reaches the intestines. Digestion of fish oil in the stomach can sometimes cause reflux action to mouth leaving the unpleased fish oil aftertaste in the mouth.
In Conclusion…
Omega-3 and fish oil supplements
carry multiple benefits for overall health. Unfortunately, with the increasing
number of evidence for omega-3 benefits, the misinformation and myths around
omega-3 and fish oil supplements have also gone up. Do not rely on the rumor
mill for information as it is full of myths that may misguide you. Keep
yourself informed and conduct your own research from reliable sources for the
best fish oil supplement. Take care in
choosing the right supplement suited to your needs and don’t fall for myths. Knowledge
of the right omega-3 source is the best way to reap the benefits of Omega-3. Use
it well!
Sources:
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5345296/
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12323090
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6117694/
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6357022/
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24859185
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16828546
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4728620/
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23317405
[9] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269551643_Omega-3_Fatty_Acids_and_Obesity
[10] https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2702216
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808858/
[12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3575932/
[13] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3976923/
[14] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17335973/
[15] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3206354/
[16] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6117694/
[17] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20848234