Omega-3 has been the buzzy term for health & fitness experts and enthusiasts alike with benefits ranging from heart, brain, joint, eye, skin and much more.
So, what are they are what are the key benefits they carry?
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Not to be confused with saturated or trans fatty acids (which are harmful to your health), Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids. They are called ‘essential’ because they are required by the body but are not produced by it and therefore must be taken through external sources.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a family of fatty acids. There are three main types of omega3 fatty acids – Alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA), Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is mostly used as an energy source while EPA & DHA are more functionally form of Omega-3 and the key reasons behind omega-3 multiple benefits. EPA & DHA are mostly found in animal or marine sources while ALA is obtained from plant sources.
Benefits of Omega-3
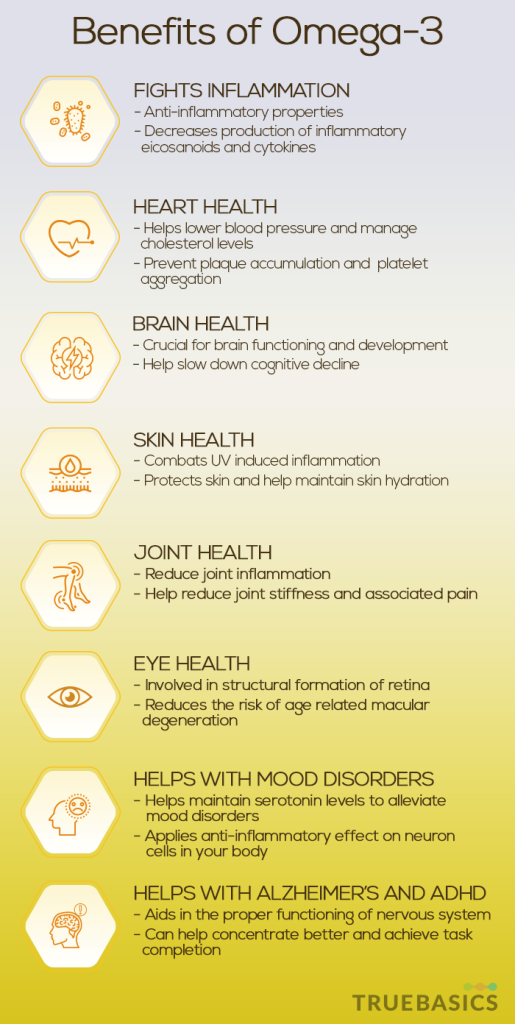
1. Fights Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s defense mechanism against foreign invaders. However, chronic inflammation can damage the health and obstruct the normal functioning of the body’s cells and tissues. Omega-3 has strong anti-inflammatory properties and help reduce the production of inflammatory eicosanoids and cytokines. It reduces inflammation by replacing the base component of inflammatory arachidonic acids which are responsible for inflammation agent production.
2. Heart Health
Omega-3 has been known to promote a healthy heart. They help reduce triglycerides levels, manage cholesterol levels in the body. High triglycerides levels are linked with fatty buildup in the artery walls. They also reduce plaque accumulation in the arteries, prevent blood platelets from aggregating and help regulate heartbeat.
3. Brain Health
Omega-3, particularly DHA, is crucial for the functioning and development of the brain. DHA is accumulated in the brain cells in the first couple of years of an infant child and help with cognitive development. Omega-3 also helps slow down cognitive decline and prevent brain aging.
4. Skin Health
Omega-3 plays a major role in maintaining skin health. Exposure to UV rays in the sunlight induces an inflammatory response in the skin causing irritation. Omega-3, owing to its anti-inflammatory properties, protects the skin cells from the UV-induced inflammation.
Omega-3 also works as a barrier to retain moisture within the skin keeping it hydrated. The presence of omega-3 in cells strengthens the skin cell membranes of the epidermis and can help fight wrinkles and acne.
5. Joint Health
Inflammation is one of the common causes of joint pain. Chronic inflammation in joints can lead to stiffness and acute pain in the joints. Omega-3 can help reduce joint inflammation and thus relieving joint pain and stiffness.
6. Eye Health
Omega-3 forms an integral structural component of the retina and is essential for the development of the infant retina. DHA is also a major constituent of tissues of the eyes. Omega-3 also helps reduce dry eye symptoms and protects eyes from inflammation. Omega-3 can also reduce the risk of Age-related macular degeneration and help relieve eye discomfort.
7. Helps with Mood Disorders
Mood disorders, among other factors, are also caused by issues with nerve signaling or nervous system dysfunction. DHA can affect the serotonin receptors of the body. Serotonin is produced by nerve cells to regulate mood. Low- levels of serotonin often manifest themselves in the form of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. DHA also helps reduce the presence of brain inflammation and help alleviate depression symptoms.
8. Helps with Alzheimer’s and ADHD
DHA is present in cell membranes of the brain and plays a key role in nervous system functioning. Omega-3 can help in the proper functioning of the nervous system and is particularly useful for Alzheimer’s patients. Studies have reported a correlation between a significant decline in brain functioning and a lack of DHA. Omega-3 is also noted to increase the flow of blood to the brain while performing the mental tasks, keeping the brain functioning normally.
What is the adequate daily dose of omega-3?
There is no recommended daily requirement set for omega-3 consumption. Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) also recommends increasing the intake of omega-3 but no RDA values have been set. The daily requirement of omega-3 varies depending on multiple factors such as age, gender, diet, lifestyle and medical health condition. Environmental and genetic variables also affect the metabolism of omega-3.
Various governments and health organizations recommend a dietary intake of 1400 to 2500 mg per day of total omega-3, with EPA and DHA content ranging from 140 to 650 mg per day for healthy adults. A higher amount of omega-3 is recommended for people with medical conditions and pregnant women and people.
The omega-3 requirement can be determined by taking a blood test that evaluates the omega-3 index. The omega-3 index is a measurement of the relative EPA and DHA amount in the red blood cells. It is expressed as the percentage of the total fatty acids present. For e.g., If the omega-index is 4, it means 4% of the total fatty acids in red blood cells are omega-3 (i.e. EPA and DHA). The omega-3 index can help determine adequate omega-3 requirements.
The omega-3 requirement is higher in cases such as –
Heart Conditions
Scientific studies have shown a positive role of omega-3 fatty acids in patients with heart diseases. For patients with coronary heart diseases, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends 1000 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily. In patients with hypertriglyceridemia, a daily dose of 2000 – 4000 mg of combined EPA and DHA is recommended.
Anxiety & Depression
It has been observed in scientific studies that omega-3 plays a role in the reduction of inflammation and anxiety in adults. Omega-3 supplements in a dose range of 200 to 2200 mg/day have been found to be effective against mood disorders such as depression.
Pregnant and Lactating Women
DHA is very important to be consumed during and after pregnancy. DHA is critical for the brain and retina development of the fetus and for proper brain functioning. Consult your doctor for the right dosage of omega-3. Average daily intake of a minimum 200 mg DHA is recommended for pregnant and lactating women. The National Institute of Health (NIH) recommends 1400 mg of ALA in pregnant women and 1300 mg of ALA in lactating or breastfeeding women. Many guidelines recommend 50-100 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily in infants and children.
How much Omega-3 is safe?
The safe limit of omega-3 consumption is a frequently asked question for omega-3. Just as there have been no RDA values set for omega-3 intake, there is no set upper limit for omega-3 as well. However, FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regards dosage of Omega-3 up to 3000 mg daily as safe whereas the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) regards up to 5000 mg daily as safe dosage.
So, while there has been no official limit set for omega-3 consumption, you should take care not to include too much omega-3. Although such high doses may not be required for all, 3000-5000 mg of omega-3 daily dosage seems to be safe.
So, what will happen if you take too much omega-3?
- Omega-3 has strong anti-inflammatory properties and can lead to a reduction in the function of the immune system as it reduces inflammatory responses of the body.
- Excess omega-3 can lead to blood thinning. You should stop taking omega-3 supplements 1-2 weeks before surgery as they can lead to an increase in bleeding time. Also, some omega-3 supplements (like cod liver oil) are high in vitamin A which is toxic in large amounts (more than 10000 mcg).
In case you are consuming omega-3 supplements, oxidative stability is generally the greater concern of the dosage. Fatty acids in fish oil are prone to oxidative rancidity which leads to foul smell. It is important to check the freshness of the product to avoid the consumption of a rancid product which can be harmful. It is thus recommended to consume high quality, check the date and smell of the supplements before buying.
How to get an adequate daily dose of Omega-3?
Omega-3 can be obtained through dietary sources. Plant sources provide us with ALA, whereas marine/animal sources are rich in EPA & DHA. Top dietary sources of omega-3 include –
1. Animal Dietary Sources
Marine sources such as fatty fishes and seafood are a rich source of EPA and DHA form of omega-3. Fatty fishes are also low in saturated fats and a good protein source. Top marine sources of omega-3 are:
- Mackerel – 5134 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Salmon – 2260 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Herring – 2366 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Anchovies – 1478 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Sardines – 1480 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
2. Plant Dietary Sources
Nuts, seeds, fruits, plant oils are a rich source of ALA form of omega-3. Top sources include –
- Flaxseed – 22813 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Chia seeds – 17552 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Canola Oil – 7636 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Walnuts – 2000 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
- Soybeans – 1330 mg omega-3 per 100 g serving
Omega-3 Fish Oil Supplements
Consumption of fatty fishes is recommended at least twice per week. However, this is not possible for the majority of the Indian population due to lifestyle preferences, absence of good quality fish as well as financial constraints. Vegans and vegetarians are especially prone to missing out on right omega-3 intake because plant sources include only ALA and little EPA/DHA. The recurring issue with consuming omega-3 rich sources regularly makes intake of Omega-3 supplement necessary.
If you are unable to fulfill your daily omega-3 requirement from the food sources, then you can consider taking omega-3 supplements. The supplements primarily contain EPA and DHA, the functionally active form of omega-3. Check the source of omega-3 in the supplement suited as per your preference – fish oil or vegan source. Choose the right omega-3 supplement suited to your lifestyle and dietary preference. Consult with a doctor, if needed, to find out the recommended dosage amount for you.

In Conclusion…
Omega-3 presents multiple health benefits for overall wellbeing. The adequate daily dose of omega-3 requirement depends on factors such as age, gender, and health condition. While no RDA values have been set for omega-3 intake, experts recommend 1000 – 2000 mg of daily omega-3 with higher amounts for medical conditions.
The daily requirement of omega-3 can be fulfilled by incorporating fatty marine sources such as fatty fishes and plant sources such as flaxseed, walnuts. As the conversion process of ALA to EPA/DHA is inefficient and very small, it is advised to consume EPA and DHA directly through fatty fish and/or omega-3 supplements. If consuming fatty fish is not an option for you, supplements could be taken in order to meet the adequate omega-3 acid requirement. Choose the right supplement which fulfills your daily requirement and helps repeat the multiple benefits of omega-3 fatty acids.
Ensure a healthy life with an adequate daily intake of Omega-3!
Sources:
[1] http://www.nationalacademies.org/hmd/~/media/Files/Activity%20Files/Nutrition/DRI-Tables/8_Macronutrient%20Summary.pdf
[2] https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.atv.0000057393.97337.ae?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21784145-omega-3-supplementation-lowers-inflammation-and-anxiety-in-medical-students-a-randomized-controlled-trial/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21939614-meta-analysis-of-the-effects-of-eicosapentaenoic-acid-epa-in-clinical-trials-in-depression/
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17493949-dietary-fatty-acids-and-colorectal-cancer-a-case-control-study/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2710648-fish-consumption-and-breast-cancer-risk-an-ecological-study/
[7] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cbin.10806
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5736071/
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9811313-nutritional-and-socioeconomic-factors-in-relation-to-prostate-cancer-mortality-a-cross-national-study/
[10] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18184094-the-roles-of-long-chain-polyunsaturated-fatty-acids-in-pregnancy-lactation-and-infancy-review-of-current-knowledge-and-consensus-recommendations/
[11] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28466678-omega-3-fatty-acids-supplementation-in-alzheimers-disease-a-systematic-review/
[12] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18408140-the-importance-of-the-omega-6omega-3-fatty-acid-ratio-in-cardiovascular-disease-and-other-chronic-diseases/