Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are known as ‘essential fats’ because your body cannot produce them and therefore have to be sourced from dietary sources to meet the daily requirement.
Omega-3
fatty acids play key roles in holistic human growth and development. There are
three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid)
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid)
While ALA is usually stored for energy, EPA and DHA play imperative roles in heart, brain, eyes and joint health. [1]
Wondering
why are EPA & DHA important for a healthy life? Let’s dive right in to
understand their role in your body.
What are EPA and DHA?
EPA is a form of omega-3 fatty acids, mostly found in foods like salmon, shrimp, mackerel, tuna, and other forms of fatty fish. EPA is converted from ALA in the human body. However, the process is inefficient and only up to 20% of ALA is converted into EPA. EPA plays an important role in reducing cellular inflammation. EPA inhibits the supply of arachidonic acid which is necessary for the production of inflammatory eicosanoids. EPA also helps in reducing neuro-inflammation [2] which are responsible for mood disorders like depression, anxiety, etc.
DHA, on the other hand, is a form of omega-3 fatty acids that is largely responsible for the structural component of the brain and the retina of the eyes [3]. DHA, too, can be converted from ALA within your body. However, the conversion rate is even lower for DHA with only up to 9% ALA getting converted. Therefore, the marine sources like mackerel, sardines, salmon, anchovies are the best sources of DHA.
Role of EPA and DHA
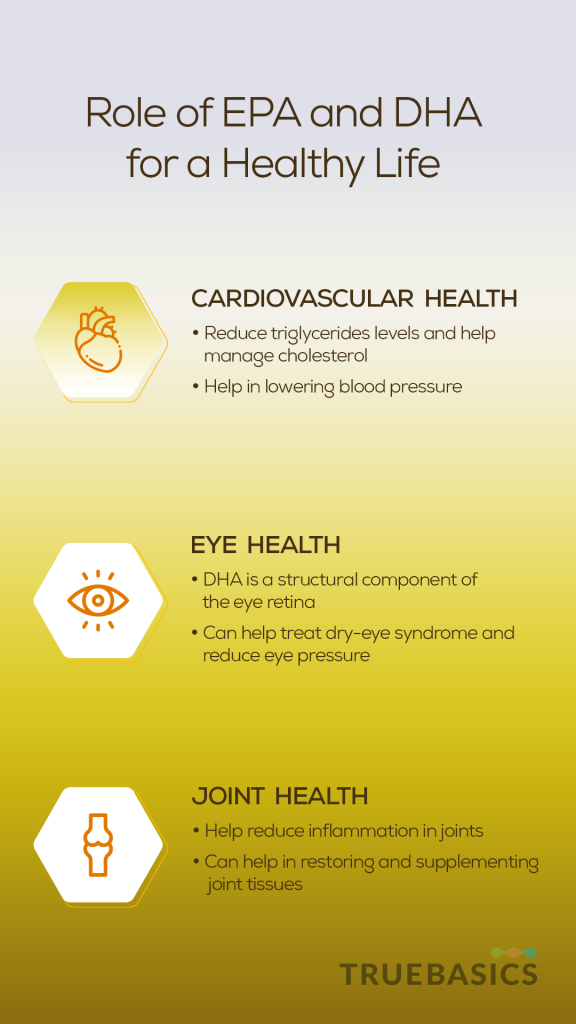
1. Cardiovascular Health
EPA & DHA help maintain a healthy heart and cardiovascular system. EPA & DHA help maintain cholesterol levels by reducing the levels of triglyceride and increasing the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL or “Good” Cholesterol).
EPA and DHA also help prevent blockages by decreasing platelet aggregation in the blood thus providing protection against coronary artery diseases. [4] EPA helps improve blood flow by dilating the blood vessels.
EPA and DHA can also help lower blood pressure levels in the body. Studies have shown that DHA reduces diastolic blood pressure while EPA reduces the systolic blood pressure, thus reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke. [5] EPA and DHA have been linked to a decreased risk of recurrent coronary artery disease and cardiac arrests [6]. Both EPA and DHA can also help reduce the abnormal rhythm of the heart. [7]
Chronic inflammation is also a major factor behind cardiovascular disease like heart attack, heart failure, coronary artery disease. EPA and DHA, owing to their anti-inflammatory properties, play an effective role in managing oxidative stress and improving cellular functions.
2. Eye Health
DHA is a major structural component involved in the formation of the retina. If your body doesn’t have enough omega-3 fatty acids, then it may increase the risk of developing vision problems like dry eyes and glaucoma. DHA and EPA can help treat dry eye syndromes with their anti-inflammatory properties. Some studies have also suggested that the anti-inflammatory nature of DHA can reduce the risk of glaucoma and discomfort caused by contact lens. [8]
EPA and DHA can also help reduce eye discomfort. A randomized clinical trial showed that patients who consumed EPA and DHA in their daily diet reported improved discomfort in the eye by up to 42% [9].Eye pressure is also said to reduce when you consume omega-3 fatty acids in adequate amounts every day.
3. Joint Health
Omega-3 is an important nutrient for people with joint pains or arthritis. The EPA and DHA in omega-3 help reduce inflammation in joints, thus relieving stiffness. Omega-3 also strengthens your bones by increasing Vitamin D levels to reduce urinary excretion of calcium, thus boosting calcium levels to enhance bone strength. This also decreases the risk of osteoporosis [10] [11]. Both EPA and DHA are also said to control the synthesis of negative proteins that can cause different types of arthritis.
EPA and DHA also help in maintaining joint health by restoring and supplementing the joint tissues. They also provide the joints with proper lubrication, which eases movement and minimizes pain and strain. [12]
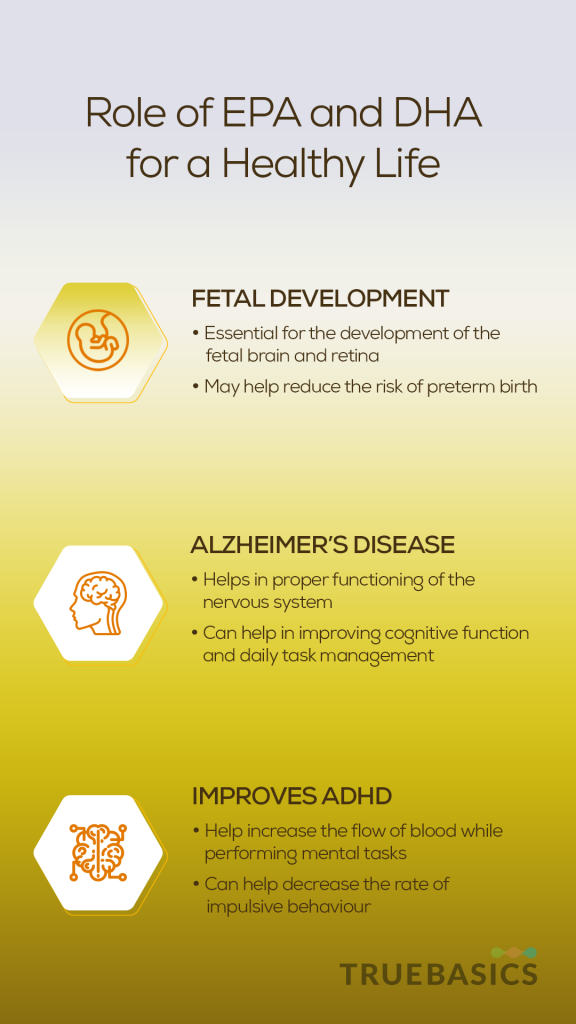
4. Fetal Development
Nutrients are transferred to the fetus through the placenta. Fetus nutrition intake is directly proportional to the mother’s nutrition values. EPA and DHA are considered important nutrients to be consumed during pregnancy due to the essential role they play for fetal development. EPA and DHA in omega-3 fatty acids are structural components of the fetus and are needed for the proper development of the retina and brain of the fetus. They’re transported all through the placenta into the fetal venous system that delivers oxygen-rich blood to the fetal heart. [13]
Studies have shown that women who consumed omega-3 during pregnancy, have also been able to protect their children from any allergies that might develop. [14]
Some studies have also suggested that EPA and DHA can also help reduce the chances of preterm birth by decreasing the production of prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2α that are a naturally occurring group of lipids that induces labor. [15]
5. Alzheimer’s Disease
DHA, particularly, present in neuron membrane phospholipids and plays a major role in the proper functioning of the nervous system. Therefore, DHA is particularly useful for Alzheimer’s patients and helps in the proper functioning of the nervous system. Studies have reported a correlation between a lack of DHA in the diet with a significant decline in brain functioning and hindrance in performing daily activities. [16]
Weight loss is also a common problem in AD patients. Regular intake of EPA and DHA has shown positive results in helping AD patients maintain weight. [17]
6. Improves ADHD
ADHD or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is a condition that causes you to behave impulsively and makes it difficult for you to concentrate. This condition is generally said to develop in early childhood and might also continue into adulthood [18]. Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, help increase the flow of blood while performing mental tasks [19]. This helps in keeping the brain functioning properly.
A randomized, double-blind study on children aged 7-9 years reported that children suffering from ADHD showed an 8% decrease in the rate of their impulsive behavior when they included DHA in their daily diet [20]. However, the full scale of the benefit is still a matter of further research.
In Conclusion…
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are extremely essential for overall health and development. They’re known to aid in joint health, reduce inflammation, prevent various heart diseases and help in conditions like ADHD and Alzheimer’s disease.
Make sure to include omega-3 rich food sources, especially fatty fish or fish oil, in your daily diet. Omega-3 can be added to the daily diet through easily accessible sources. Choose the right omega-3 source or supplement as per your lifestyle and requirement to lead a healthy life and age gracefully.
Sources:
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20439549
[3] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02859265
[4] https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.114.015176
[5] https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[7] https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.015176
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29477134
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30046817
[10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9932142
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9624425
[12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4965662/
[13] https://www.hindawi.com/journals/tswj/2012/202473/
[14] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[15] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[16] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[17] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
[18] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27217152
[19] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27217152
[20] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22970149